Pillar 4 - Gut Health
Meerensee Medical Centre
Pillar 4 – Gut Health. More and more research is going into Gut Health. Increasing amount of studies are indicating that the gut seems to play a vital role in many aspects of our health.
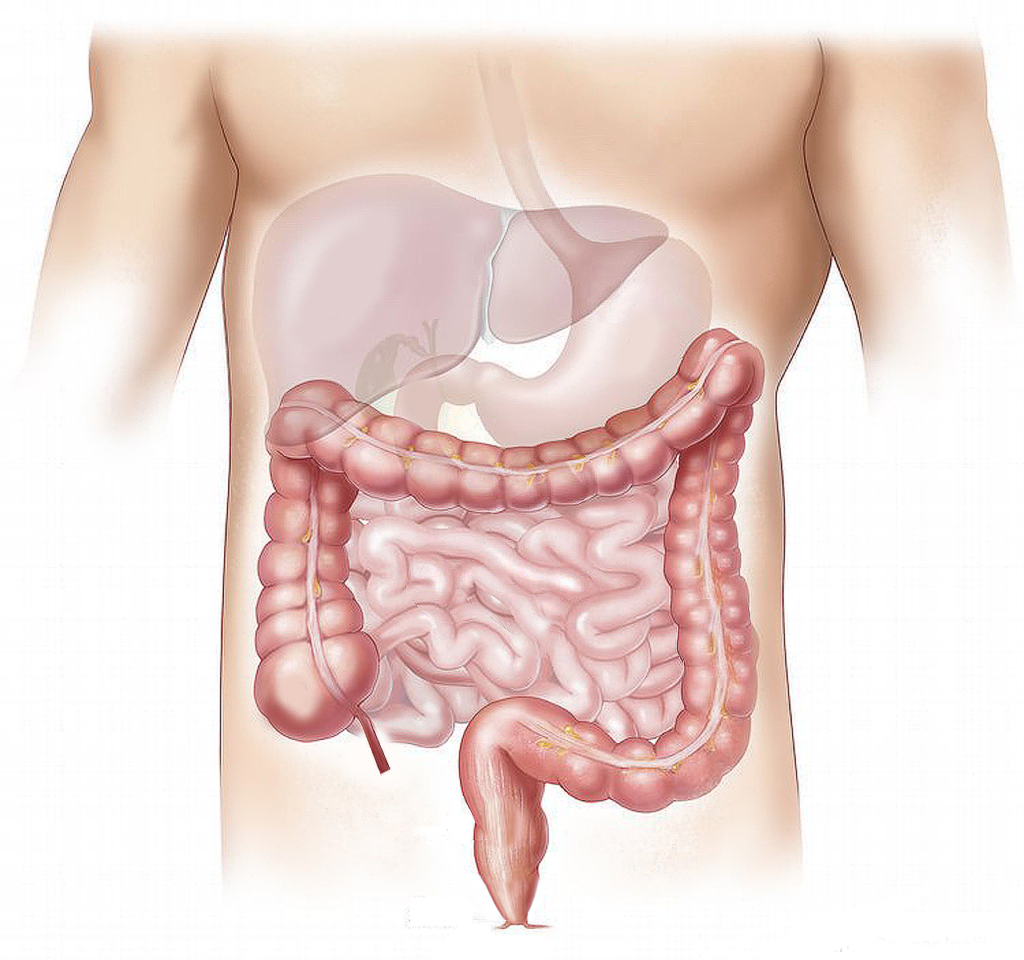
Why is Gut Health Important?
The correct microbiome (good bacteria) can play a vital role in your well being.
It assists in the digestion of food as well as the absorption of nutrients, vitamins and minerals. If your gut microbiome is imbalanced, there is bad bacteria or yeast overgrowth. The processes mentioned above gets affected. This can result in a poor immune system, chronic inflammation, bloating, constipation, hormonal imbalances, brain fog and feelings of tiredness.
The gut gets rid of metabolic waste and toxins. Constipation can therefore result in fecal stasis, toxins being absorbed into the blood stream as well as an overgrowth of the bad bacteria.
How to Improve your Gut Health
- Remove Sugar and processed foods from your diet
- Increase your Fiber content
- Take a Good Pro-Biotic
- Introduce Sauerkraut, Kefir, Kombucha and Kimchi into your diet.
Food Allergies vs Food Sensitivities / Intolerances
Definition
Food Allergy – The offending food causes an immune response, which triggers a range of symptoms, which can be severe or life-threatening. Symptoms of food allergy include hives, swelling, itching, anaphylaxis, and dizziness.
Food Intolerance often affects only the digestive system and causes less serious symptoms. Generally there is a lack of an enzyme to digest the food.
Symptoms of food intolerance are generally the same as food sensitivity. Intolerance is more serious than sensitivity. The most common foods that people are intolerant too are dairy and gluten. Symptoms of food intolerance include gas, bloating, diarrhoea, constipation, cramping, and nausea.
Lactose intolerance. It’s caused by a deficiency in the enzyme that digest lactose. If you suffer from lactose intolerance, you may be able to alleviate symptoms by taking an over-the-counter enzyme replacement such as Lactaid.
Gluten sensitivity. Gluten is a protein found in the grains wheat, barley, and rye. In some people, consumption of these grains leads to celiac disease, which is an autoimmune condition, not a food allergy or food intolerance. In other people, the grains seem to cause symptoms of food intolerance, but not the intestinal damage that characterises celiac disease. The only current treatment for gluten sensitivity is avoiding all gluten-containing grains.
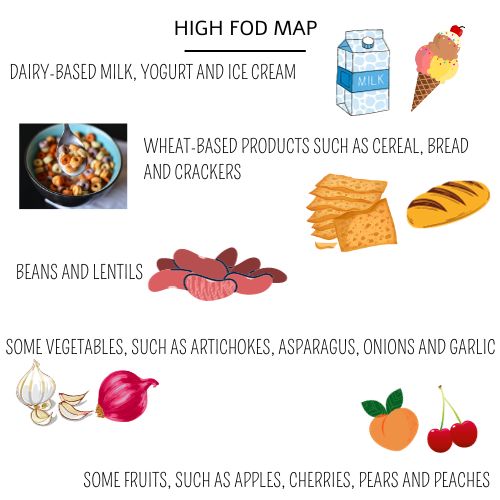
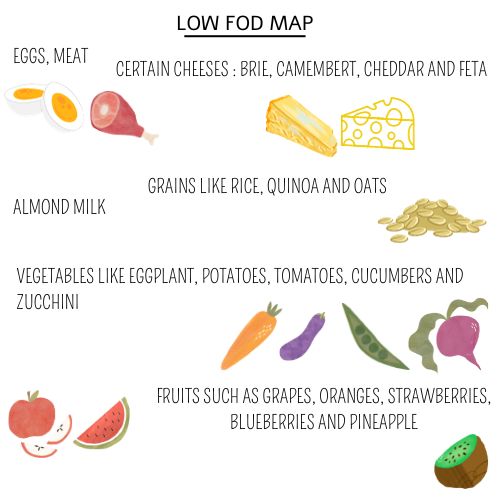
Low Fod Map Diet
- FODMAP diet means a diet low in FODMAP — certain sugars that may cause intestinal distress. This diet is designed to help people with irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and/or small intestinal bacterial overgrowth (SIBO) figure out which foods are problematic and which foods reduce symptoms.
FODMAP stands for fermentable oligosaccharides, disaccharides, monosaccharides and polyols, which are short-chain carbohydrates, that the small intestine absorbs poorly. These sugars cannot be broken down in the small intestine, thus they enter the large intestine, the bacteria from the colon feeds on them, producing gas and fatty acids.
Symptoms include:
- Cramping
- Diarrhoea
- Constipation
- Stomach bloating
- Flatulence
Low FODMAP is a three-step elimination diet:
- Stop eating high FODMAP foods for 2 – 6 weeks.
- Then, reintroduce them one at a time, every 3 days, to see which ones are troublesome.
- Once the foods that cause symptoms are identified, avoidance of these foods, will improve symptoms.
How can my Doctor help?
Dietary changes can have a big impact on IBS and SIBO symptoms. Antibiotics can reduce small intestinal bacterial overgrowth, while laxatives and low-dose antidepressants can relieve symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome.
Generally, a person needs a combination of dietary changes, medications and stress management